How to write a business plan for a general practitioner practice?

Putting together a business plan for a general practitioner practice can be daunting - especially if you're creating a business for the first time - but with this comprehensive guide, you'll have the necessary tools to do it confidently.
We will explore why writing one is so important in both starting up and growing an existing general practitioner practice, as well as what should go into making an effective plan - from its structure to content - and what tools can be used to streamline the process and avoid errors.
Without further ado, let us begin!
Why write a business plan for a general practitioner practice?
Being clear on the scope and goals of the document will make it easier to understand its structure and content. So before diving into the actual content of the plan, let's have a quick look at the main reasons why you would want to write a general practitioner practice business plan in the first place.
To have a clear roadmap to grow the business
Running a small business is tough! Economic cycles bring growth and recessions, while the business landscape is ever-changing with new technologies, regulations, competitors, and consumer behaviours emerging constantly.
In such a dynamic context, operating a business without a clear roadmap is akin to driving blindfolded: it's risky, to say the least. That's why crafting a business plan for your general practitioner practice is vital to establish a successful and sustainable venture.
To create an effective business plan, you'll need to assess your current position (if you're already in business) and define where you want the business to be in the next three to five years.
Once you have a clear destination for your general practitioner practice, you'll have to:
- Identify the necessary resources (human, equipment, and capital) needed to reach your goals,
- Determine the pace at which the business needs to progress to meet its objectives as scheduled,
- Recognize and address the potential risks you may encounter along the way.
Engaging in this process regularly proves advantageous for both startups and established companies. It empowers you to make informed decisions about resource allocation, ensuring the long-term success of your business.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

To anticipate future cash flows
Regularly comparing your actual financial performance to the projections in the financial forecast of your general practitioner practice's business plan gives you the ability to monitor your business's financial health and make necessary adjustments as needed.
This practice allows you to detect potential financial issues, such as unexpected cash shortfalls before they escalate into major problems. Giving you time to find additional financing or put in place corrective measures.
Additionally, it helps you identify growth opportunities, like excess cash flow that could be allocated to launch new products and services or expand into new markets.
Staying on track with these regular comparisons enables you to make well-informed decisions about the amount of financing your business might require, or the excess cash flow you can expect to generate from your main business activities.
To secure financing
Crafting a comprehensive business plan for your general practitioner practice, whether you're starting up or already established, is paramount when you're seeking financing from banks or investors.
Given how fragile small businesses are, financiers will want to ensure that you have a clear roadmap in place as well as command and control of your future cash flows before entertaining the idea of funding you.
For banks, the information in your business plan will be used to assess your borrowing capacity - which is defined as the maximum amount of debt your business can afford alongside your ability to repay the loan. This evaluation helps them decide whether to extend credit to your business and under what terms (interest rate, duration, repayment options, collateral, etc.).
Similarly, investors will thoroughly review your plan to determine if their investment can yield an attractive return. They'll be looking for evidence that your general practitioner practice has the potential for healthy growth, profitability, and consistent cash flow generation over time.
Now that you understand the importance of creating a business plan for your general practitioner practice, let's delve into the necessary information needed to craft an effective plan.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

Information needed to create a business plan for a general practitioner practice
You need the right data in order to project sales, investments and costs accurately in the financial forecast of your general practitioner practice business plan.
Below, we'll cover three key pieces of information you should gather before drafting your business plan.
Carrying out market research for a general practitioner practice
As you consider writing your business plan for a general practitioner practice, conducting market research becomes a vital step to ensure accurate and realistic financial projections.
Market research provides valuable insights into your target customer base, competitors, pricing strategies, and other key factors that can significantly impact the commercial success of your business.
Through this research, you may uncover trends that could influence your general practitioner practice.
You might discover that people may be more likely to prefer booking appointments online rather than over the phone. Additionally, market research could reveal that people might be more likely to seek out alternative forms of medical care, such as naturopathy or acupuncture, alongside their visits to the GP.
Such market trends play a significant role in forecasting revenue, as they offer valuable data about potential customers' spending habits and preferences.
By incorporating these findings into your financial projections, you can present investors with more accurate information, helping them make informed decisions about investing in your general practitioner practice.
Developing the sales and marketing plan for a general practitioner practice
As you embark on creating your general practitioner practice business plan, it is crucial to budget sales and marketing expenses beforehand.
A well-defined sales and marketing plan should include precise projections of the actions required to acquire and retain customers. It will also outline the necessary workforce to execute these initiatives and the budget required for promotions, advertising, and other marketing efforts.
This approach ensures that the appropriate amount of resources is allocated to these activities, aligning with the sales and growth objectives outlined in your business plan.
The staffing and equipment needs of a general practitioner practice
Whether you are at the beginning stages of your general practitioner practice or expanding its horizons, having a clear plan for recruitment and capital expenditures (investment in equipment and real estate) is vital to ensure your business's success.
To achieve this, both the recruitment and investment plans must align coherently with the projected timing and level of growth in your forecast. It is essential to secure appropriate funding for these plans.
Staffing costs for a general practitioner practice may include salaries for receptionists, nurses, and doctors, as well as benefits and vacation pay. Equipment costs may include exam tables, medical equipment, and diagnostic tools such as X-ray machines, as well as computers and software for medical records.
To create a financial forecast that accurately represents your business's outlook, remember to factor in other day-to-day operating expenses.
Now that you have all the necessary information, it's time to dive in and start creating your business plan and developing the financial forecast for your general practitioner practice.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

What goes into your general practitioner practice's financial forecast?
The objective of the financial forecast of your general practitioner practice's business plan is to show the growth, profitability, funding requirements, and cash generation potential of your business over the next 3 to 5 years.
The four key outputs of a financial forecast for a general practitioner practice are:
- The profit and loss (P&L) statement,
- The projected balance sheet,
- The cash flow forecast,
- And the sources and uses table.
Let's look at each of these in a bit more detail.
The projected P&L statement
The projected P&L statement for a general practitioner practice shows how much revenue and profits your business is expected to generate in the future.
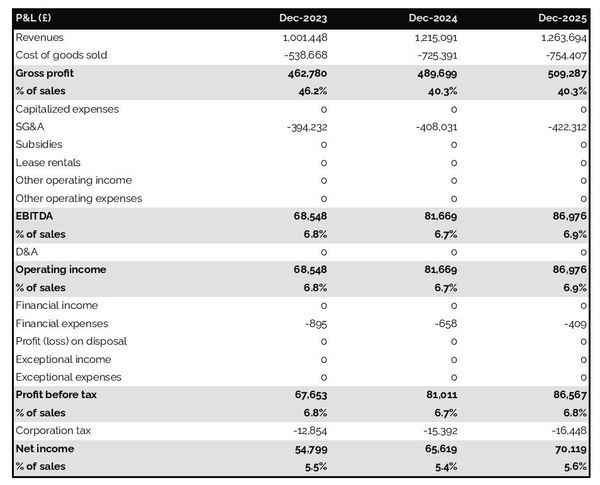
Ideally, your general practitioner practice's P&L statement should show:
- Healthy growth - above inflation level
- Improving or stable profit margins
- Positive net profit
Expectations will vary based on the stage of your business. A startup will be expected to grow faster than an established general practitioner practice. And similarly, an established company should showcase a higher level of profitability than a new venture.
The projected balance sheet of your general practitioner practice
The balance sheet for a general practitioner practice is a financial document that provides a snapshot of your business’s financial health at a given point in time.
It shows three main components: assets, liabilities and equity:
- Assets: are resources owned by the business, such as cash, equipment, and accounts receivable (money owed by clients).
- Liabilities: are debts owed to creditors and other entities, such as accounts payable (money owed to suppliers) and loans.
- Equity: includes the sums invested by the shareholders or business owners and the cumulative profits and losses of the business to date (called retained earnings). It is a proxy for the value of the owner's stake in the business.
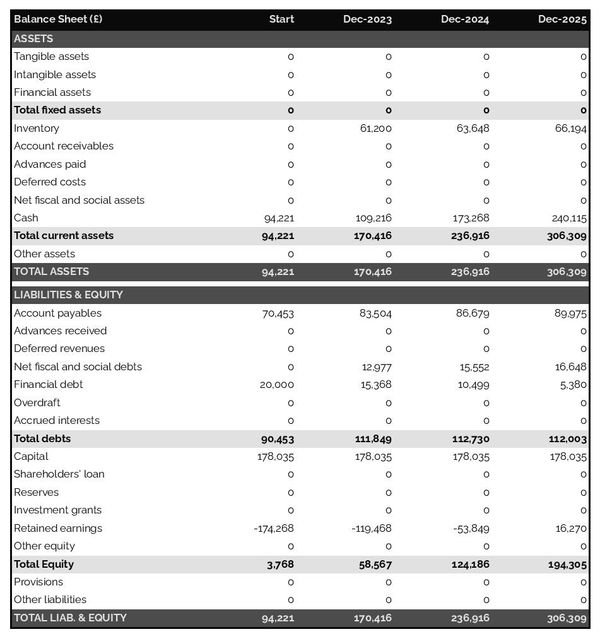
Examining the balance sheet is important for lenders, investors, or other stakeholders who are interested in assessing your general practitioner practice's liquidity and solvency:
- Liquidity: assesses whether or not your business has sufficient cash and short-term assets to honour its liabilities due over the next 12 months. It is a short-term focus.
- Solvency: assesses whether or not your business has the capacity to repay its debt over the medium-term.
Looking at the balance sheet can also provide insights into your general practitioner practice's investment and financing policies.
In particular, stakeholders can compare the value of equity to the value of the outstanding financial debt to assess how the business is funded and what level of financial risk has been taken by the owners (financial debt is riskier because it has to be repaid, while equity doesn't need to be repaid).
The cash flow forecast
As we've seen earlier in this guide, monitoring future cash flows is the key to success and the only way of ensuring that your general practitioner practice has enough cash to operate.
As you can expect showing future cash flows is the main role of the cash flow forecast in your general practitioner practice business plan.
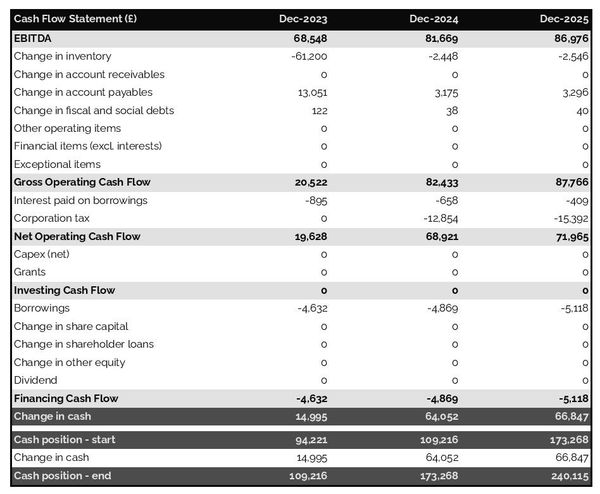
It is best practice to organise the cash flow statement by nature in order to show the cash impact of the following areas:
- Cash flow generated from operations: the operating cash flow shows how much cash is generated or consumed by the business's commercial activities
- Cash flow from investing activities: the investing cash flow shows how much cash is being invested in capital expenditure (equipment, real estate, etc.) either to maintain the business's equipment or to expand its capabilities
- Cash flow from financing activities: the financing cash flow shows how much cash is raised or distributed to financiers
Looking at the cash flow forecast helps you to make sure that your business has enough cash to keep running, and can help you anticipate potential cash shortfalls.
Your general practitioner practice business plan will normally include both yearly and monthly cash flow forecasts so that the readers can view the impact of seasonality on your business cash position and generation.
The initial financing plan
The initial financing plan, also known as a sources and uses table, is a valuable resource to have in your business plan when starting your general practitioner practice as it reveals the origins of the money needed to establish the business (sources) and how it will be allocated (uses).
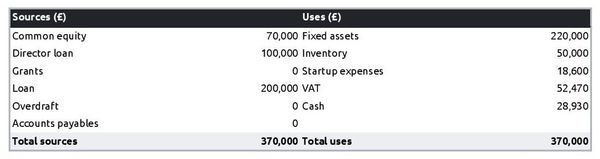
Having this table helps show what costs are involved in setting up your general practitioner practice, how risks are shared between founders, investors and lenders, and what the starting cash position will be. This cash position needs to be sufficient to sustain operations until the business reaches a break-even point.
Now that you have a clear understanding of what goes into the financial forecast of your general practitioner practice business plan, let's shift our focus to the written part of the plan.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

The written part of a general practitioner practice business plan
The written part of a general practitioner practice business plan is composed of 7 main sections:
- The executive summary
- The presentation of the company
- The products and services
- The market analysis
- The strategy
- The operations
- The financial plan
Throughout these sections, you will seek to provide the reader with the details and context needed for them to form a view on whether or not your business plan is achievable and your forecast a realistic possibility.
Let's go through the content of each section in more detail!
1. The executive summary
The executive summary, the first section of your general practitioner practice's business plan, serves as an inviting snapshot of your entire plan, leaving readers eager to know more about your business.
To compose an effective executive summary, start with a concise introduction of your business, covering its name, concept, location, history, and unique aspects. Share insights about the services or products you intend to offer and your target customer base.
Subsequently, provide an overview of your general practitioner practice's addressable market, highlighting current trends and potential growth opportunities.
Then, present a summary of critical financial figures, such as projected revenues, profits, and cash flows.
You should then include a summary of your key financial figures such as projected revenues, profits, and cash flows.
Lastly, address any funding needs in the "ask" section of your executive summary.
2. The presentation of the company
As you build your general practitioner practice business plan, the second section deserves attention as it delves into the structure and ownership, location, and management team of your company.
In the structure and ownership part, you'll provide valuable insights into the legal structure of the business, the identities of the owners, and their respective investments and ownership stakes. This level of transparency is vital, particularly if you're seeking financing, as it clarifies which legal entity will receive the funds and who holds the reins of the business.
Moving to the location part, you'll offer a comprehensive view of the company's premises and articulate why this specific location is strategic for the business, emphasizing factors like catchment area, accessibility, and nearby amenities.
When describing the location of your general practitioner practice, you could emphasize its potential for growth. It may be near a rising population center, with a growing number of potential customers. It could also be in a desirable neighborhood, with easy access to public transportation and other amenities. You might also highlight the area's low crime rate, high average incomes, and other attractive features that could make the location an attractive investment.
Lastly, you should introduce your esteemed management team. Provide a thorough explanation of each member's role, background, and extensive experience.
It's equally important to highlight any past successes the management team has achieved and underscore the duration they've been working together. This information will instil trust in potential lenders or investors, showcasing the strength and expertise of your leadership team and their ability to deliver the business plan.
3. The products and services section
The products and services section of your business plan should include a detailed description of what your company offers, who are the target customers, and what distribution channels are part of your go-to-market.
For example, your general practitioner practice might offer physical exams, immunizations, and prescription refills as products and services to its customers. Physical exams allow customers to track their health and identify any potential issues that may arise. Immunizations help protect customers from serious illnesses. Prescription refills ensure that customers are able to take the medications necessary to maintain their health.
4. The market analysis
When you present your market analysis in your general practitioner practice business plan, it's crucial to include detailed information about customers' demographics and segmentation, target market, competition, barriers to entry, and any relevant regulations.
The main objective of this section is to help the reader understand the size and attractiveness of the market while demonstrating your solid understanding of the industry.
Begin with the demographics and segmentation subsection, providing an overview of the addressable market for your general practitioner practice, the key trends in the marketplace, and introducing different customer segments along with their preferences in terms of purchasing habits and budgets.
Next, focus on your target market, zooming in on the specific customer segments your general practitioner practice aims to serve and explaining how your products and services fulfil their distinct needs.
For example, your target market might include young people aged 18-30 who live in the surrounding area. These customers may require general check-ups, vaccinations, and other routine medical care. They may also be more likely to take advantage of preventative care services, such as nutrition counseling and smoking cessation programs.
Then proceed to the competition subsection, where you introduce your main competitors and highlight what sets you apart from them.
Finally, conclude your market analysis with an overview of the key regulations applicable to your general practitioner practice.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

5. The strategy section
When crafting the strategy section of your business plan for your general practitioner practice, it's important to cover several key aspects, including your competitive edge, pricing strategy, sales & marketing plan, milestones, and risks and mitigants.
In the competitive edge subsection, clearly explain what sets your company apart from competitors. This is particularly critical if you're a startup, as you'll be trying to establish your presence in the marketplace among entrenched players.
The pricing strategy subsection should demonstrate how you aim to maintain profitability while offering competitive prices to your customers.
For the sales & marketing plan, outline how you plan to reach and acquire new customers, as well as retain existing ones through loyalty programs or special offers.
In the milestones subsection, detail what your company has achieved thus far and outline your primary objectives for the coming years by including specific dates for expected progress. This ensures everyone involved has clear expectations.
Lastly, in the risks and mitigants subsection, list the main risks that could potentially impact the execution of your plan. Explain the measures you've taken to minimize these risks. This is vital for investors or lenders to feel confident in supporting your venture - try to proactively address any objection they might have.
Your general practitioner practice may face risks related to patient safety. For example, the practice could be exposed to potential legal liability in the event of a medical malpractice incident. Additionally, the practice might be exposed to financial risks if they are unable to collect payments from insurance companies or patients.
6. The operations section
The operations of your general practitioner practice must be presented in detail in your business plan.
Begin by addressing your staff, specifying the main roles and your recruitment plan to support the anticipated growth. Outline the qualifications and experience needed for each role and discuss your recruitment strategies, which may involve using job boards, referrals, or headhunters.
Next, clearly state your general practitioner practice's operating hours, allowing the reader to gauge the adequacy of your staffing levels. Additionally, mention any considerations for varying opening times during peak seasons and your approach to handling customer queries outside regular operating hours.
The key assets and intellectual property (IP) required to run your business should also be highlighted. If you rely on licenses, trademarks, physical structures like equipment or property, or lease agreements, ensure they are well-documented in this section.
You may have key assets such as patient records and financial records. These may be stored electronically and could be particularly sensitive and important to the practice. Additionally, the practice might have intellectual property such as patient contact information and records of treatments, which could be valuable to the practice and its continued operation.
Finally, provide a comprehensive list of suppliers you intend to collaborate with, along with a breakdown of their services and main commercial terms, such as price, payment terms, break clauses and contract duration. Investors often seek insight into the reasons behind your supplier choices, which may include a preference for higher-quality products or established relationships from past ventures.
7. The presentation of the financial plan
The financial plan section is where we will include the financial forecast we talked about earlier in this guide.
Now that you have a clear idea of the content of a general practitioner practice business plan, let's look at some of the tools you can use to create yours.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

What tool should I use to write my general practitioner practice's business plan?
In this section, we will be reviewing the two main solutions for creating a general practitioner practice business plan:
- Using specialized online business plan software,
- Outsourcing the plan to the business plan writer.
Using an online business plan software for your general practitioner practice's business plan
Using online business planning software is the most efficient and modern way to create a general practitioner practice business plan.
There are several advantages to using specialized software:
- You can easily create your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can access a library of dozens of complete business plan samples and templates for inspiration
- You get a professional business plan, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank or investors
- You can easily track your actual financial performance against your financial forecast
- You can create scenarios to stress test your forecast's main assumptions
- You can easily update your forecast as time goes by to maintain visibility on future cash flows
- You have a friendly support team on standby to assist you when you are stuck
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try The Business Plan Shop for free by signing up here.
Hiring a business plan writer to write your general practitioner practice's business plan
Outsourcing your general practitioner practice business plan to a business plan writer can also be a viable option.
These writers possess valuable experience in crafting business plans and creating accurate financial forecasts. Additionally, enlisting their services can save you precious time, enabling you to concentrate on the day-to-day operations of your business.
It's important to be mindful, though, that hiring business plan writers comes with a cost. You'll be paying not just for their time but also for the software they use, and their profit margin.
Based on experience, a complete business plan usually requires a budget of at least £1.5k ($2.0k) excluding tax, and more if revisions are needed after initial meetings with lenders or investors - changes often arise following these discussions.
When seeking investment, be cautious about spending too much on consulting fees. Investors prefer their funds to contribute directly to business growth. Thus, the amount you spend on business plan writing services and other consulting services should be negligible compared to the amount you raise.
Another aspect to consider is that while you'll receive the output of the business plan, you usually won't own the actual document. It will be saved in the consultant's business plan software, which will make updating the plan challenging without retaining the consultant on a retainer.
Given these factors, it's essential to carefully weigh the pros and cons of outsourcing your general practitioner practice business plan to a business plan writer and decide what best suits your business's unique needs.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

Why not create your general practitioner practice's business plan using Word or Excel?
Using Microsoft Excel and Word (or their Google, Apple, or open-source equivalents) to write a general practitioner practice business plan is not advisable. Allow me to explain the reasons.
Firstly, creating an accurate and error-free financial forecast on Excel or any spreadsheet demands technical expertise in accounting principles and financial modelling. Without a degree in finance and accounting and significant financial modelling experience, it's unlikely that the reader will fully trust your numbers.
Secondly, relying on spreadsheets is inefficient. While it may have been the go-to option in the past, technology has evolved, and software now performs such tasks much faster and more accurately.
The second reason is that it is inefficient. Building forecasts on spreadsheets was the only option in the early 2000s, nowadays technology has advanced and software can do it much faster and much more accurately.
And with the rise of AI, software is also becoming smarter at helping us detect mistakes in our forecasts and helping us analyse the numbers to make better decisions.
Moreover, software offers ease in comparing actuals versus forecasts and maintaining up-to-date forecasts for clear visibility on future cash flows, as we discussed earlier in this guide. Such tasks are cumbersome when using spreadsheets.
Now, let's address the written part of your general practitioner practice business plan. While it may be less prone to errors, using software can significantly boost productivity. Word processors lack instructions and examples for each section of your business plan. They also won't automatically update your numbers when changes occur in your forecast, and they lack automated formatting capabilities.
In summary, while some entrepreneurs may consider Word or Excel for their business plan, it's far from the best or most efficient solution when compared to specialized software.
Takeaways
- Having an up-to-date business plan is key to maintaining visibility on your future cash flows.
- A business plan has 2 parts: a financial forecast highlighting the expected growth, profitability and cash generation of the business; and a written part which provides the context needed to interpret and assess the quality of the forecast.
- Using business plan software is the modern way of writing and maintaining business plans.
We hope that this guide helped you to better understand how to write the business plan for a general practitioner practice. If you still have questions, do not hesitate to contact us.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- How to write a 5 years business plan
- How to write a 3-year business plan?
- Business plan financial projections
- Difference between business model canvas and business plan
- Business plan myths
Know someone who owns or wants to start a general practitioner practice? Share this article with them!