How to format a business plan and make it look good?

Business plans are important documents that help entrepreneurs convince business partners, investors and other stakeholders. The document contains valuable strategic and financial information about the business.
In this guide, we’ll zoom in on the formatting of a business plan, covering everything from the cover page to the appendix, whilst also including helpful tips. By the end of the guide, you’ll have a much better idea of how to create a presentable and professional business plan.
Ready? Let’s get started!
How to format your business plan cover page?
Your business plan cover page is the first thing that readers will see. This means that it is the first impression they’ll have about your business.
So, you need to make it look professional and well-formatted.
Arguably, the most important thing that needs to be on the cover page of your business plan is your company name and logo. It allows you to portray your brand identity and will probably help make a lasting impression.
The logo should be clearly visible, but you should still leave enough space for your contact information:
- Main contact
- Their phone number
- Their email address

Adding this information will help the audience learn what your business is called and how you can be contacted if needed. In addition, the cover page should also include the date on which the business plan was last updated.
Providing this information lets the audience know that all of the strategic details and financial forecasts mentioned in the document are recent and accurate.
Lastly, you need to make sure that your business plan cover page color scheme is "on-brand" and aligns with your corporate identity.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

How to format your business plan executive summary?
Now that you know how to format the cover page, let’s look at the executive summary. The executive summary serves as an overview of the entire document, providing key strategic and financial information about the business.
Having a well-written and formatted executive summary is critical because stakeholders such as investors, often have multiple business plans to read. As a result, any executive summary that looks incompetent will likely result in the business plan being discarded.

When writing the document, you need to make sure that the executive summary is located at the beginning. It should go right after the cover page and table of contents. This will provide the reader with all the necessary information required to decide whether to continue reading or not.
An executive summary is more than a short blurb about the business. In fact, there are four key subsections - let’s have a look at each one in more detail:
Business overview
This is the first part of the executive summary. Here, you will have to write an engaging overview of the business. The overview should thoroughly explain what the business is, what it does, your concept, and who you sell to.
Market analysis
In this section, you should summarize the findings of your market research. Be sure to include the market size, any recent trends, your target market, and business opportunities.
Financial highlights
This section will help readers get an idea of the size and historical performance of your business (or how big your idea aims to be) and give a glimpse of the expected growth and profitability for the years to come.
To do this, you can include a table with your key financials and KPIs. You should also add commentary explaining the expected profitability for each year along with other key metrics such as EBITDA and revenues.
Funding requirements
If the aim of your business plan is to seek funding, then this is the section where you’ll mention the amount you need. Be sure to provide a list of ways the capital will be used and what investors (or lenders) can expect to get in return.
How to format the body of your business plan?
Once the executive summary is done, you’ll need to format the body of the business plan.
The body contains all of the key editorial information and financials that readers will want to see.
This should include the following:
- Company Overview
- Products or Services
- Market Analysis
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Operations and Management
- Financial Projections
- Funding Request
- Appendices
Fonts and headings
Ensuring consistency throughout each of these sections is highly important. You need to make sure that the font type, size, headings, sub-headings, and body text remain the same throughout.
If possible, try to stay on-brand and use the main color of your coporate identity for the main headings and the ascent colour for the subheads.
Make sure the font size large enough, this will depend on the type or family of font used but something between 10 and 14 should normaly be enough.
It is also recommended to use a sans-serif font type such as Arial or Roboto for main text in order to ensure best readability.
Spacing and margins
Pay attention to the line height and spacing before and after each paragraph, these need to be both consistent throughout, and large enough so that the text doesn't appear cramped.
Leave generous margins to facilitate the reading of the document if printed. Left and right margins need to be wide enough to allow for the document to be held and bound without covering the text.
Header and footer
Each section should also include a header and a footer. Inside the header, you can add the title of that particular section for reference. In the footer, there must be a page number that is referenced in the table of content.
Breaking up the text
When formatting the body of the document you should use visual aids such as graphs, charts, tables, and diagrams. These can help present complex information more effectively and break the text making the overall document easier to read and more appealing.
Remember, each visual aid you add to the document must be properly labelled and sources referenced when quoting external sources or data.
In addition to this, you could also use bulleted or numbered lists to present information in a concise and organized manner. These lists help break up text-heavy sections and improve readability.
Lastly, it’s important to ensure that the tone and writing style of the document is professional and formal throughout the content. In addition, you should also proofread the entire document once completed.

How to format the financial projections in your business plan?
The financial projections section of your business plan is very important because lenders and investors use this section to assess the viability of your business and make informed decisions.
When formatting the financial projection section, you need to do the following:
Create separate subsection to present each financial statement
Financial data is quite complex, and including all of the information in a single section can make it challenging for the reader to understand. Therefore, we recommend to break this information into separate subsections.
Financial statements in a business plan include (at a minimum):
- a projected balance sheet
- a cash flow forecast
- a projected profit and loss (P&L) statement
- a sources and uses table (for a business startup)
- a breakeven point calculation
- historical financials (for an existing business)
Clearly indicate the timelines and frequency used for financial data in the statements
When adding financial statements, you must ensure that the reader is clear on what period of time is included in each column.
The market practice is to label the column with the month and year of the end of the period covered ("Jun-2024" for example).
We recommend avoiding using letter to designate quarters ("Q1", "Q2", "Q3", "Q4") or half-years ("HY1 2023", "HY2 2023") as these can create confusion as whether these are relative to the calendar year of the financial year of the company.
For yearly data, you can use the abbreviations: "CY" for calendar year, "FY" for financial year (or "FYE" for financial year ending), or "TY" for tax year. For example "FYE Jan-2025" for a company with an financial year ending in January.
When approaching foreign investors, be weary of localisation differences: depending where you are 07/08/2023 could either mean the 7th of August or the 8th of July. Using letters for the month make things clearer.
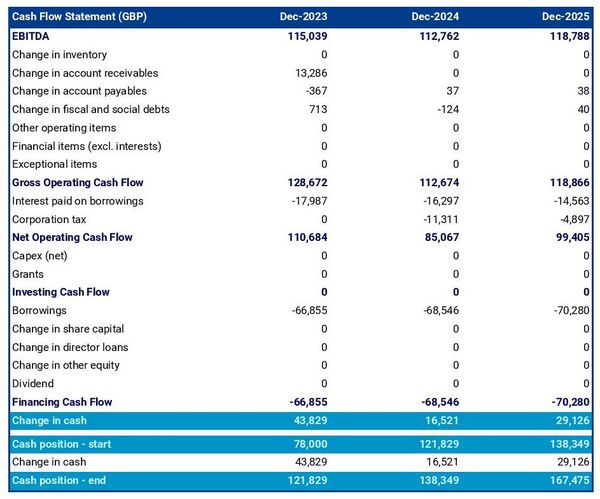
If you combine forecasted and historical financial data, you should also label each column appropriately so that the reader is clear on what type of data is included. There are a couple ways to do so:
- You can do so by adding "Actuals" for historical data and "Forecasted" for projected data below the label with the date,
- Or you can add a capital "F" after the date of forecasted data: "Jun-2024 F" for example.
Also don't hesitate to specify which frequency has been used when there is a risk of confusion. An easy way to to do is to add the frequency in the title of the section or table. For example "Yearly P&L" or "Monthly cash flow forecast".
Mention the currency and unit used for financial data in the tables
We also recommend clearly specifying which unit and currency have been used.
For the currency, you can use either the currency symbol or the 3 letters ISO code. We recommend using the ISO code when the reader might not be familiar with your currency symbol (foreign investor for example), or when there is a risk of confusion - for example it is better to write AU$ or AUD than $ if you are using the Australian dollar.
If you converted your numbers to a different currency (for example in US$ when sending your plan to a US investor) or if your business sells in multiple currencies, it is also important to clearly quote the exchange rate used both for forecasted and historical data (for example: "Data using exchange rate of €1.0000 = £0.8533 as of 07 July 2023").
We also recommend indicating which unit has been used. You can do so by using standard abbreviations such as:
- Data in k or '000 to designate thousands
- Data in m or millions to designate millions
- Data in bn or billions to designate billions
Use standard formatting for numbers
When presenting numbers in financial statements it is standard to:
- Use 2 decimals for prices
- Use a thousand separator and 1 decimal for amounts
- Use 1 decimal for percentages (growth, margin, yields) and format them in x when the value is above 100%. 2.5x growth for 250.0%, for example.
- Use 1 or 2 decimals for ratios (DSO, multiples, etc.)
There is a bit more lattitude when it comes to the actual number format, you can either:
- Use standard notation: 12,345.6 for positive and -12,345.6 for negative numbers
- Use accounting notation: 12,345.6 for positive and (12,345.6) for negative numbers
- Use '0' or '-' for zeroes
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

How to format the appendices of your business plan?
Most entrepreneurs overlook the appendices section of the business plan. In truth, however, it’s probably as important as the main body of the document as it provides supporting documents for the reader, some of which may have been requested.
Supporting documents that are commonly attached to appendices include:
- CVs of the management team
- Credit histories
- Licenses
- Patents
- Other legal documents
- Monthly details for financial data
- External data used or referenced in the business plan
These documents can help justify certain claims you’ve made whilst writing the business plan. They also help ensure that the main body of the business plan reads cohesively without being bogged down by additional documents and details.
When adding these documents to the business plan, it’s important that they have a dedicated section of their own. Each appendix or supporting document should have a clear document and title explaining its purpose.
In addition, it should also include a description of each document. In the description, you can mention the importance of the appendix, its validity (if applicable), and other details that are necessary.
After adding the appendices, you need to make sure each of them is numbered accurately. Finally, you need to provide a reference to the relevant document in the appropriate section of the business plan.
For example, in the products and services section, if you were to reference the patents attached as supporting documents, you might write something like “Please see appendix 4.6 for more details”.
Business plan formatting tips
Now that you’ve learned how to format your business plan entirely from the cover page to the appendices, let’s look at some valuable formatting tips.
1. First impressions last
Make sure your cover page is well-designed. The design should align with your corporate identity. The cover page should also present information such as the company name and contact details.
2. Avoid writing a text-heavy business plan
Adding images, charts, and graphs to make your document more appealing. This also helps make the document more comprehensive and improves readability.
3. Avoid using outdated tools to create a business plan
Whilst Word and Excel are great business tools, they’re only effective for creating simple documents. Creating a presentable business plan using these tools is quite tedious.
A much better idea is to use online business plan software.
There are several advantages to using specialized software:
- You get a professional document, formatted automatically following the best practices discussed in this guide, and ready to be sent to your bank
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can be inspired by already written business plan templates
- You can easily make your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- The software will enable you to easily track your actual financial performance against your forecast and update your forecast as time goes by
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try our software for free by signing up here.
Conclusion
Business plans are very important documents for entrepreneurs and established businesses alike. They serve many purposes, like helping find business partners or securing capital.
The document contains strategic and financial details about the business. This information can help readers decide whether they want to be a stakeholder in your business or not.
The business plan must be formatted properly to ensure better readability. Using our business plan software can help you create an appealing and effective document with ease.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- How investors analyse business plans
- Where to write the conclusion of your business plan?
- Business plan length
- Business plan vs business proposal
- Strategic plan and business plan