How to create a financial forecast for a language school?

If you are serious about keeping visibility on your future cash flows, then you need to build and maintain a financial forecast for your language school.
Putting together a language school financial forecast may sound complex, but don’t worry, with the right tool, it’s easier than it looks, and The Business Plan Shop is here to guide you.
In this practical guide, we'll cover everything you need to know about building financial projections for your language school.
We will start by looking at why they are key, what information is needed, what a forecast looks like once completed, and what solutions you can use to create yours.
Let's dive in!
Why create and maintain a financial forecast for a language school?
The financial projections for your language school act as a financial blueprint to guide its growth with confidence and ensure its long-term financial viability.
To create them, you will need to look at your business in detail - from sales to operating costs and investments - to assess how much profit it can generate in the years to come and what will be the associated cash flows.
During challenging market conditions, maintaining an up-to-date financial forecast enables early detection of potential financial shortfalls, allowing for timely adjustments or securing financing before facing a cash crisis.
Your language school's financial forecast will also prove invaluable when seeking financing. Banks and investors will undoubtedly request a thorough examination of your financial figures, making precision and presentation essential.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

What information is needed to build a language school financial forecast?
The quality of your inputs is key when it comes to financial modelling: no matter how good the model is, if your inputs are off, so will the forecast.
If you are building a financial plan to start a language school, you will need to have done your market research and have a clear picture of your sales and marketing strategies so that you can project revenues with confidence.
You will also need to have a clear idea of what resources will be required to operate the language school on a daily basis, and to have done your research with regard to the equipment needed to launch your venture (see further down this guide).
If you are creating a financial forecast of an existing language school, things are usually simpler as you will be able to use your historical accounting data as a budgeting base, and complement that with your team’s view on what lies ahead for the years to come.
Let's now zoom in on what will go in your language school's financial forecast.
The sales forecast for a language school
From experience, it usually makes sense to start your language school's financial projection with the revenues forecast.
The inputs used to forecast your sales will include the historical trading data of your language school (which can be used as a starting point for existing businesses) and the data collected in your market research (which both new ventures and existing businesses need to project their sales forward).
Your language school's sales forecast can be broken down into two key estimates:
- The average price
- The number of monthly transactions
To assess these variables accurately, you will need to consider the following factors:
- Seasonal demand: You may see fluctuations in your average price and number of monthly transactions based on the time of year. For example, during summer months when students have more free time, you may see an increase in demand for language courses, resulting in higher prices and more transactions.
- Economic conditions: Changes in the economy can also affect your average price and number of monthly transactions. For instance, if there is a recession, people may be less likely to spend money on language courses, resulting in lower prices and fewer transactions.
- Competition: The presence of other language schools in your area can impact your average price and number of monthly transactions. If there is a lot of competition, you may need to lower your prices to stay competitive, resulting in lower average prices but potentially more transactions.
- Student demographics: The demographics of your target audience can also affect your average price and number of monthly transactions. For example, if you primarily cater to adults looking to advance their career, you may be able to charge higher prices compared to catering to students looking to learn a language for personal interest.
- Partnerships: Collaborating with other businesses or organizations can also impact your average price and number of monthly transactions. Partnering with a local company to offer language courses to their employees, for example, may result in higher prices and more transactions.
Once you have a sales forecast in place, the next step will be to work on your overhead budget. Let’s have a look at that now.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

The operating expenses for a language school
The next step is to estimate the expenses needed to run your language school on a day-to-day basis.
These will vary based on the level of sales expected, and the location and size of your business.
But your language school's operating expenses should include the following items at a minimum:
- Staff costs: Includes salaries, benefits, and taxes for all employees, such as teachers, administrative staff, and support staff.
- Rent: The cost of leasing or renting a physical space for the language school.
- Utilities: Expenses for electricity, water, and other utilities used in the operation of the language school.
- Office supplies: Includes paper, pens, printer ink, and other office supplies used in day-to-day operations.
- Textbooks and teaching materials: The cost of purchasing or licensing textbooks and other materials for students.
- Marketing and advertising: Expenses for promoting the language school, such as advertising, website maintenance, and promotional materials.
- Accountancy fees: The cost of hiring an accountant to handle financial record-keeping and tax preparation.
- Insurance costs: Includes liability insurance, property insurance, and other types of insurance necessary for the language school.
- Software licenses: Expenses for software used in the operation of the language school, such as learning management systems, accounting software, and office productivity tools.
- Banking fees: Charges for maintaining bank accounts and processing transactions, such as wire transfers and credit card payments.
- Professional development: The cost of training and development programs for teachers and staff to keep their skills up to date.
- Travel expenses: Includes airfare, accommodations, and other expenses related to business travel for language school staff.
- Telephone and internet: The cost of maintaining phone and internet services for the language school.
- Repairs and maintenance: Expenses for repairing and maintaining the physical space and equipment used in the language school.
- Taxes and licenses: Includes business taxes, permits, and other fees required to operate the language school.
This list is, of course, not exhaustive, and you'll have to adapt it according to your precise business model and size. A small language school might not have the same level of expenditure as a larger one, for example.
What investments are needed to start or grow a language school?
Once you have an idea of how much sales you could achieve and what it will cost to run your language school, it is time to look into the equipment required to launch or expand the activity.
For a language school, capital expenditures and initial working capital items could include:
- Classroom Equipment: This includes items such as desks, chairs, whiteboards, projectors, and other necessary equipment for teaching and learning in a language school.
- Language Learning Software: As technology continues to advance, language schools must invest in up-to-date software to provide students with the best learning experience. This may include language learning apps, online courses, and other digital resources.
- Library Resources: Language schools often have a library with a wide range of books, CDs, and other materials for students to use for self-study. These resources must be regularly updated and maintained, which can be a significant expense for the school.
- Furniture and Fixtures: This includes all the non-classroom furniture and fixtures in the school, such as reception desks, lounge chairs, and office furniture. These items not only contribute to the overall aesthetic of the school but also provide a comfortable and functional environment for students and staff.
- Language Lab Equipment: Many language schools have language labs where students can practice speaking and listening skills in a simulated environment. This requires specialized equipment such as headphones, microphones, and recording software, which can be a significant capital expense for the school.
Again, this list will need to be adjusted according to the specificities of your language school.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

The financing plan of your language school
The next step in the creation of your financial forecast for your language school is to think about how you might finance your business.
You will have to assess how much capital will come from shareholders (equity) and how much can be secured through banks.
Bank loans will have to be modelled so that you can separate the interest expenses from the repayments of principal, and include all this data in your forecast.
Issuing share capital and obtaining a bank loan are two of the most common ways that entrepreneurs finance their businesses.
What tables compose the financial plan for a language school?
Now let's have a look at the main output tables of your language school's financial forecast.
The projected profit & loss statement
The projected profit & loss shows how profitable your language school is likely to be in the years to come.
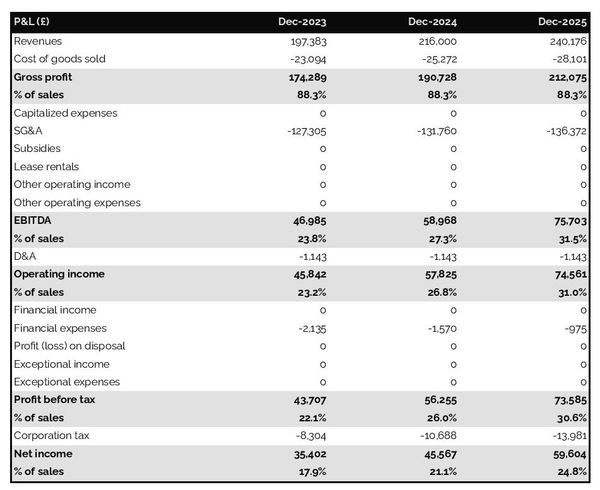
For your language school to be financially viable, your projected P&L should ideally show:
- Sales growing above inflation (the higher the better)
- Profit margins which are stable or expanding (the higher the better)
- A net profit at the end of each financial year (the higher the better)
This is for established language schools, there is some leniency for startups which will have numbers that will look a bit different than existing businesses.
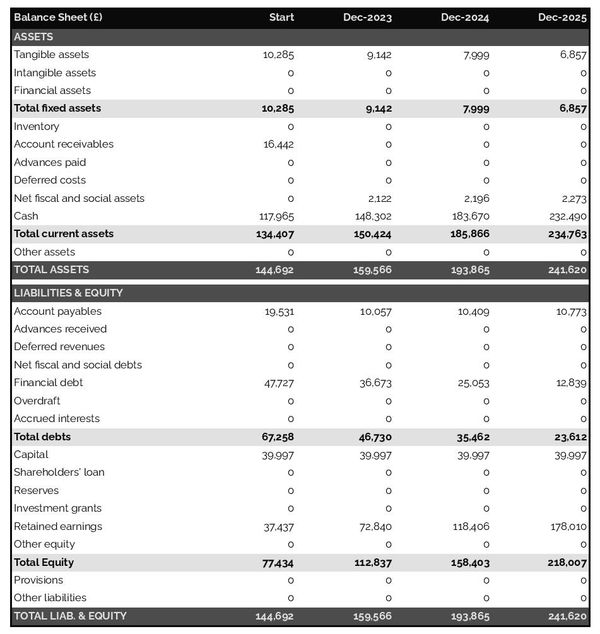
The projected balance sheet
Your language school's forecasted balance sheet enables you to assess your financial structure and working capital requirements.
It is composed of three types of elements: assets, liabilities and equity:
- Assets: represent what the business owns and uses to produce cash flows. It includes resources such as cash, equipment, and accounts receivable (money owed by clients).
- Liabilities: represent funds advanced to the business by lenders and other creditors. It includes items such as accounts payable (money owed to suppliers), taxes due and loans.
- Equity: is the combination of what has been invested by the business owners and the cumulative profits and losses generated by the business to date (which are called retained earnings). Equity is a proxy for the value of the owner's stake in the business.
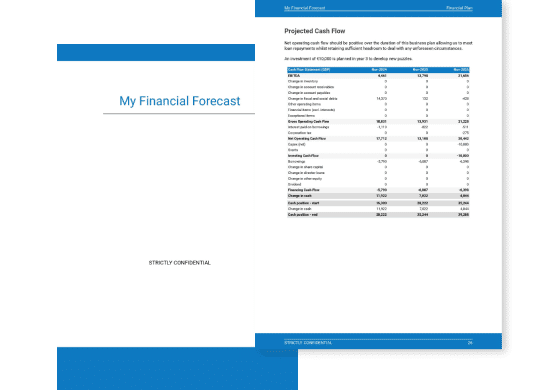
The projected cash flow statement
A projected cash flow statement for a language school is used to show how much cash the business is generating or consuming.
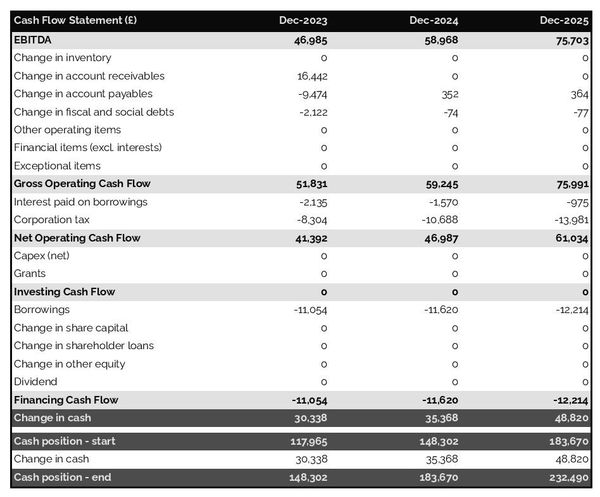
The cash flow forecast is usually organised by nature to show three key metrics:
- The operating cash flow: do the core business activities generate or consume cash?
- The investing cash flow: how much is the business investing in long-term assets (this is usually compared to the level of fixed assets on the balance sheet to assess whether the business is regularly maintaining and renewing its equipment)?
- The financing cash flow: is the business raising new financing or repaying financiers (debt repayment, dividends)?
Cash is king and keeping an eye on future cash flows is imperative for running a successful business. Therefore, you should pay close attention to your language school's cash flow forecast.
If you are trying to secure financing, note that it is customary to provide both yearly and monthly cash flow forecasts in a financial plan - so that the reader can analyze seasonal variation and ensure the language school is appropriately capitalised.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

Which tool should you use to create your language school's financial forecast?
Using the right tool or solution will make the creation of your language school's financial forecast much easier than it sounds. Let’s explore the main options.
Using online financial forecasting software to build your language school's projections
The modern and easiest way is to use professional online financial forecasting software such as the one we offer at The Business Plan Shop.
There are several advantages to using specialised software:
- You can easily create your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- You have access to complete financial forecast templates
- You get a complete financial forecast ready to be sent to your bank or investors
- You can easily track your actual financial performance against your financial forecast, and recalibrate your forecast as the year goes by
- You can create scenarios to stress test your forecast's main assumptions
- You can easily update your forecast as time goes by to maintain visibility on future cash flows
- You have a friendly support team on standby to assist you when you are stuck
- It’s cost-efficient and much cheaper than using an accountant or consultant (see below)
If you are interested in this type of solution, you can try our forecasting software for free by signing up here.
Calling in a financial consultant or chartered accountant
Outsourcing the creation of your language school financial forecast is another possible solution.
This will cost more than using software as you can expect as your price will have to cover the accountant’s time, software cost, and profit margin.
Price can vary greatly based on the complexity of your business. For a small business, from experience, a simple three-year financial forecast (including a balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement) will start at around £700 or $1,000.
Bear in mind that this is for forecasts produced at a single point in time, updating or tracking your forecast against actuals will cost extra.
If you decide to outsource your forecasting:
- Make sure the professional has direct experience in your industry and is able to challenge your assumptions constructively.
- Steer away from consultants using sectorial ratios to build their client’s financial forecasts (these projections are worthless for a small business).
Why not use a spreadsheet such as Excel or Google Sheets to build your language school's financial forecast?
You and your financial partners need numbers you can trust. Unless you have studied finance or accounting, creating a trustworthy and error-free language school financial forecast on a spreadsheet is likely to prove challenging.
Financial modelling is very technical by nature and requires a solid grasp of accounting principles to be done without errors. This means that using spreadsheet software like Excel or Google Sheets to create accurate financial forecasts is out of reach for most business owners.
Creating forecasts in Excel is also inefficient nowadays:
- Software has advanced to the point where forecasting can be done much faster and more accurately than manually on a spreadsheet.
- With artificial intelligence, the software is capable of detecting mistakes and helping decision-making.
Spreadsheets are versatile tools but they are not tailor-made for reporting. Importing your language school's accounting data in Excel to track actual vs. forecast is incredibly manual and tedious (and so is keeping forecasts up to date). It is much faster to use dedicated financial planning tools like The Business Plan Shop which are built specially for this.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

Use our financial projection templates for inspiration
The Business Plan Shop has dozens of financial forecasting templates available.
Our examples contain both the financial forecast, and a written business plan which presents, in detail, the company, the team, the strategy, and the medium-term objectives.
Whether you are just starting out or already have your own language school, looking at our template is always a good way to get ideas on how to model financial items and what to write when creating a business plan to secure funding.
Takeaways
- Having a financial forecast enables you to visualise the expected growth, profitability, and cash generation for your business over the next three to five years.
- Tracking actuals vs. forecast and keeping your financial projections up-to-date is the only way to get a view on what your language school future cash flows may look like.
- Using financial forecasting software is the mordern and easy way to create and maintain your forecasts.
This is the end of our guide on how to build the financial forecast for a language school, we hope you found it useful. Don't hesitate to contact us if you want to share your feedback or have any questions.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

Also on The Business Plan Shop
- Example of financial forecast
- Financial forecast for a business idea
- How to create a sales forecast for a business?
Know someone who owns or is thinking of starting a language school? Share our forecasting guide with them!